What is Contact Dermatitis?
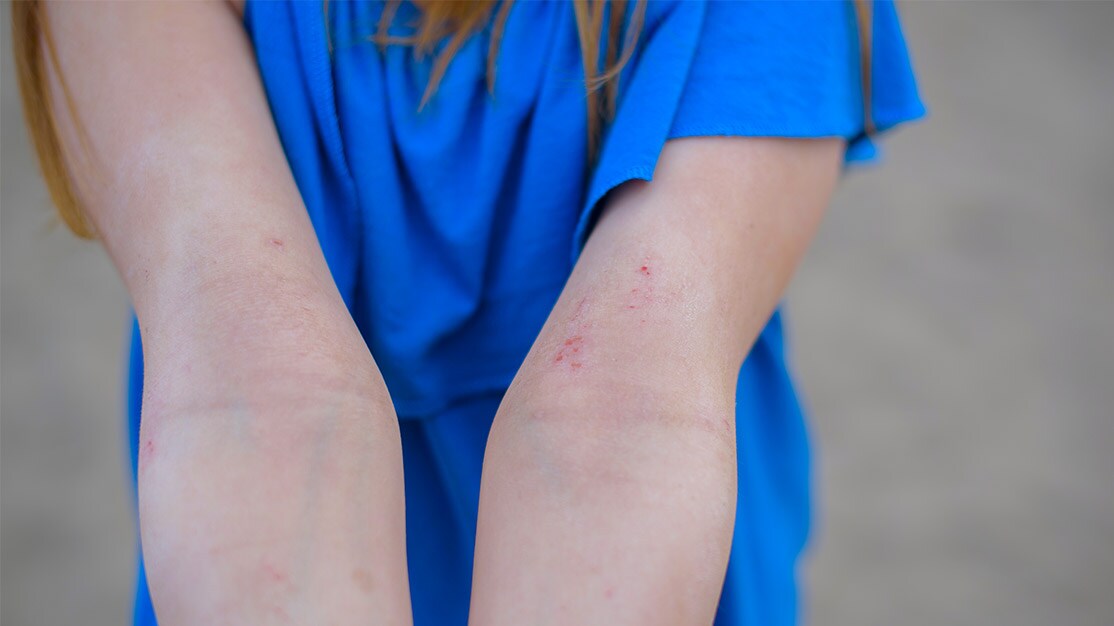
Contact dermatitis is a type of rash that develops after touching something that irritates your skin or that you are allergic to.
The skin often appears red, swollen, and may burn or feel itchy. The rash may blister. Some rashes form right away while others can take a few days or weeks to appear. Two forms of contact dermatitis include irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis. When the rash is caused by a substance that irritates the skin, it is called irritant contact dermatitis. If the rash is the result of a skin allergy, it is called allergic contact dermatitis.
Contact dermatitis symptoms vary between people and they also depend on what agent caused the reaction. The agent can be environmental, such as hot or cold temperatures, sunlight or dry humidity, an odor or airborne, like dust, smoke or pollen. Symptoms can also change over time. In most cases, symptoms only affect the area of your skin that had contact with the substance. However, the rash can spread to other parts of your body if the triggering substance is on your hands. Reactions can happen the first time you're exposed to the irritant or allergen. Or you can suddenly develop contact dermatitis from a substance you have come into contact with many times before.
What is irritant contact dermatitis?
Irritant contact dermatitis happens when the skin comes into contact with an irritant. The most common irritants are products that people use on a daily basis. These can include soap, shampoos, detergents, and rubbing alcohol. People with fair skin, dry skin or other skin conditions may be more likely to have irritant contact dermatitis. You may also have an increased risk if you work in the health care, food service or another industry that requires you to wash your hands often.
Symptoms of irritant contact dermatitis include:
- Mild irritants can cause itching, redness, dryness and small cracks in the skin.
- Stronger irritants can lead to tenderness, swelling, blisters and oozing. This type of dermatitis often affects the hands, especially between the fingers. It can also occur on the face, commonly on the eyelids.
What is allergic contact dermatitis?
Allergens are substances that cause an allergic reaction. In allergic contact dermatitis, the allergen comes into contact with your skin, which triggers your body's immune system to cause a reaction, such as itching, swelling or redness. Examples of allergens include plants like poison ivy, cosmetics, latex and nickel in jewelry, buttons or keys.
Symptoms of allergic contact dermatitis are as follows:
- Intense itching.
- Red, streaky or patchy rash with bumps or blisters that may ooze or drain and feel warm and tender. The rash typically appears within 1–2 days after you have contact with the allergen but some may take more time.
How is contact dermatitis diagnosed?
If you have symptoms of contact dermatitis, see your health care provider. They'll check your skin and ask you questions about what substances you've had contact with. It's helpful to bring a list of everything you've been exposed to or touched, and everywhere you've been over the past couple of days. In severe cases, your provider may do patch testing. This involves applying small patches of potential allergens and irritants to your skin and wearing it for a few days. After about two days, the patches are removed and your provider will check the areas for signs of a reaction. Then they'll likely check your skin again after another few days to look for a delayed reaction. Or you may have other types of testing done.
How to treat contact dermatitis
Treatment for contact dermatitis includes healing the irritated skin and avoiding the irritant or allergen so you don't have future reactions. You also shouldn't scratch your skin. Your health care provider will recommend treatment based on what's causing the reaction and the severity of your symptoms. You'll also have to throw out irritants or allergens, and you may need to wash clothes and other materials that have been exposed to the irritant or allergen.
In irritant contact dermatitis, treatment often involves washing the affected area well to remove traces of the irritant from your skin. Your provider may also suggest a moisturizer or emollient. Moisturizing can help your skin repair and protect itself from further inflammation.
In allergic contact dermatitis, your provider may recommend treatment with an oatmeal bath or soothing lotion, such as calamine lotion. In some cases, especially if the affected area is oozing fluid or crusting, your provider may tell you to apply a wet or damp dressing. This can help protect the area, ease itching, reduce redness and remove crusting.
Medications can also help contact dermatitis. Examples include antihistamines to help relieve itching and steroid creams or ointments to help reduce skin inflammation. You may need antibiotics if the skin becomes infected.
How long does contact dermatitis last?
Contact dermatitis often clears up within two to four weeks. But your symptoms can come back if you're exposed to the irritant or allergen again. If you have contact with a known irritant or allergen, wash the affected skin with soap and water right away.
Is contact dermatitis contagious?
No, contact dermatitis isn't contagious. You develop it from contact with an irritant or allergen.
Updated on February 19, 2021
Sources:
https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/eczema/contact-dermatitis
https://acaai.org/allergies/types/skin-allergies/contact-dermatitis
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000869.htm
https://www.uptodate.com/contents/contact-dermatitis-including-latex-dermatitis-beyond-the-basics
https://www.uptodate.com/contents/irritant-contact-dermatitis-in-adults?search=contact%20dermatitis&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~150&usage_type=default&display_rank=1
https://www.uptodate.com/contents/management-of-allergic-contact-dermatitis
https://nationaleczema.org/eczema/types-of-eczema/